Percutaneous Closure of PM VSD – A Minimally Invasive Alternative to Open Heart Surgery
Innovative Pediatric Cardiology Intervention at Medicover Hospitals
Patient Overview
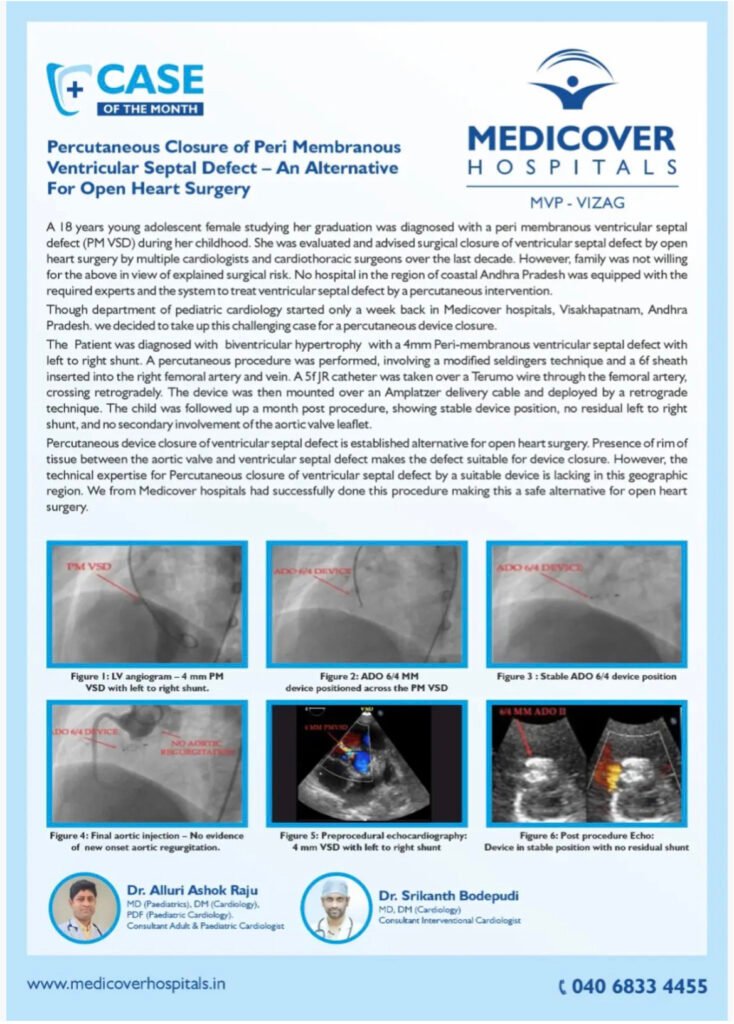
An 18-year-old female with a long-standing peri-membranous ventricular septal defect (PM VSD) was advised open-heart surgery for closure. Due to surgical risks and lack of local expertise in coastal Andhra Pradesh, her family deferred treatment—until Medicover Hospitals, Visakhapatnam, offered a groundbreaking percutaneous (non-surgical) closure as a safer alternative.
Visual Evidence
Expert team
Led by Dr. Alluri Ashok Raju (Pediatric Cardiologist) and Dr. Srikanth Bodepudi (Interventional Cardiologist), this case highlights Medicover’s commitment to cutting-edge, patient-centric care.
Percutaneous closure of Ruptured sinus of Valsalva (RSOV)– A novel structural heart intervention as an alternative for high-risk open-heart surgery.
Innovative Pediatric Cardiology Intervention at Medicover Hospitals
Patient Overview
Age: 33 years
Gender: Male
Residence: Kakinada, India
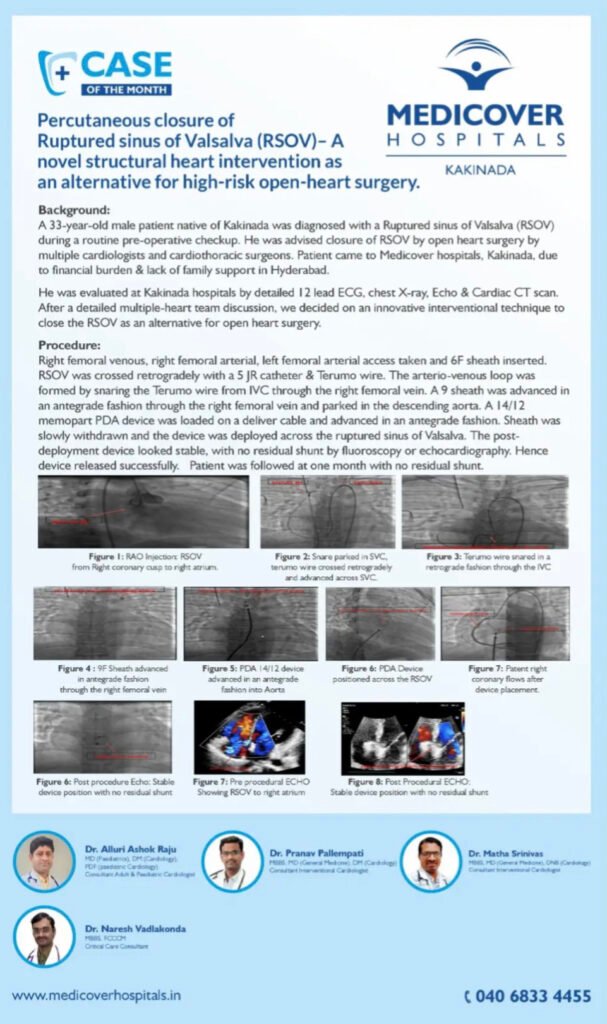
Diagnosis: Ruptured Sinus of Valsalva (RSOV) from the Right Coronary Cusp into the Right Atrium.
Presenting Scenario:
The patient’s condition was discovered incidentally during a routine pre-operative checkup for an unspecified procedure. The RSOV is a rare cardiac defect where a tear develops in one of the aortic sinuses, creating an abnormal connection (in this case, to the right atrium).
Initial Treatment Recommendations:
Multiple cardiologists and cardiothoracic surgeons advised open-heart surgery as the standard treatment to close the defect.
Visual Evidence
Expert team
Expert Medical Team
1. Dr. Alluri Ashok Raju
Qualifications: MD (Paediatrics), DM (Cardiology), PDF (Paediatric Cardiology)
Role: Consultant Adult & Paediatric Cardiologist
Note: Dr. Raju is the common lead specialist across both cases, highlighting expertise in both adult structural heart interventions and complex paediatric congenital heart disease.
2. Dr. Pranav Pallempati
Qualifications: MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Cardiology)
Role: Consultant Interventional Cardiologist
Note: Part of the core interventional cardiology team for the first adult case (RSOV closure).
3. Dr. Matha Srinivas
Qualifications: MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Cardiology)
Role: Consultant Interventional Cardiologist
Note: Part of the core interventional cardiology team for the first adult case (RSOV closure).
4. Dr. Naresh Vadlakonda
Qualifications: MBBS, FICCM
Role: Critical Care Consultant
Note: Provided critical care support for the first adult case, essential for managing patient stability during and after the high-risk procedure.
This team demonstrates a multi-disciplinary approach, combining:
Advanced Interventional Cardiology for performing complex percutaneous procedures.
Specialised Paediatric Cardiology for managing congenital heart defects in children.
Critical Care Medicine for comprehensive peri-operative patient management.
Simultaneous PDA + ASD Closure In A Child With Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension : Managing Challenging Hemodynamics.
Innovative Pediatric Cardiology Intervention at Medicover Hospitals
Patient Overview
Age: 3 years
Gender: Female
Weight: 9.5 kg
Presenting Symptoms: Recurrent respiratory tract infections and failure to thrive (inadequate weight gain and growth).
Key Physical Finding: A continuous heart murmur with a loud pulmonary component, indicative of significant pulmonary hypertension.
Diagnosis:
The child was diagnosed with two congenital heart defects:
A large Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
An associated Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Both defects resulted in severe pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) with pressures at near-systemic levels.
Treatment History:
A previous attempt to close the PDA at another facility was abandoned due to the high, systemic-level pulmonary artery pressures, which posed a significant surgical risk.
Chosen Treatment Pathway:
The patient underwent a simultaneous percutaneous transcatheter closure of both the PDA and the ASD. This approach was chosen to test the reversibility of the pulmonary hypertension.
The PDA was closed first with a 14/12 mm device, which led to a significant drop in pulmonary pressure.
Following this improvement, the ASD was closed with a 10 mm device, which resulted in a further decline in pulmonary pressure to a much safer range.
Outcome:
The procedure was successful. Post-procedure hemodynamics showed a dramatic improvement, with mean pulmonary artery pressure dropping from 84 mmHg to 37 mmHg. The patient was discharged on oral Sildenafil (a medication to treat pulmonary hypertension) and showed symptomatic improvement at the one-month follow-up.
Key Takeaway:
This case demonstrates that even in children with severe pulmonary hypertension, transcatheter device closure of defects can be a safe and effective treatment option. Closing the defects can test and often lead to a significant reversal of the high pulmonary pressures, avoiding the need for high-risk open-heart surgery.
Visual Evidence

Expert team
Lead Specialist:
Dr. Alluri Ashok Raju
Qualifications: MD (Paediatrics), DM (Cardiology), PDF (Paediatric Cardiology)
Role: Consultant Adult & Paediatric Cardiologist
Note: Dr. Raju is the named lead specialist for this complex paediatric case. His advanced training in both general cardiology (DM) and paediatric cardiology (PDF) is specifically suited for performing this simultaneous device closure on a young child with severe pulmonary hypertension.
While the document specifically names Dr. Raju for this case, a procedure of this complexity (simultaneous PDA and ASD closure in a high-risk patient) would typically involve a multi-disciplinary team in the catheterization lab, which could include:
Other Interventional Cardiologists
Anaesthesiologists
Cardiac Nurses
Echocardiography Sonographers
Radiographers
However, based solely on the text provided in this specific image, Dr. Alluri Ashok Raju is the explicitly identified expert.
